Key resources
All the documents you need for your RS GCSE.
Course title
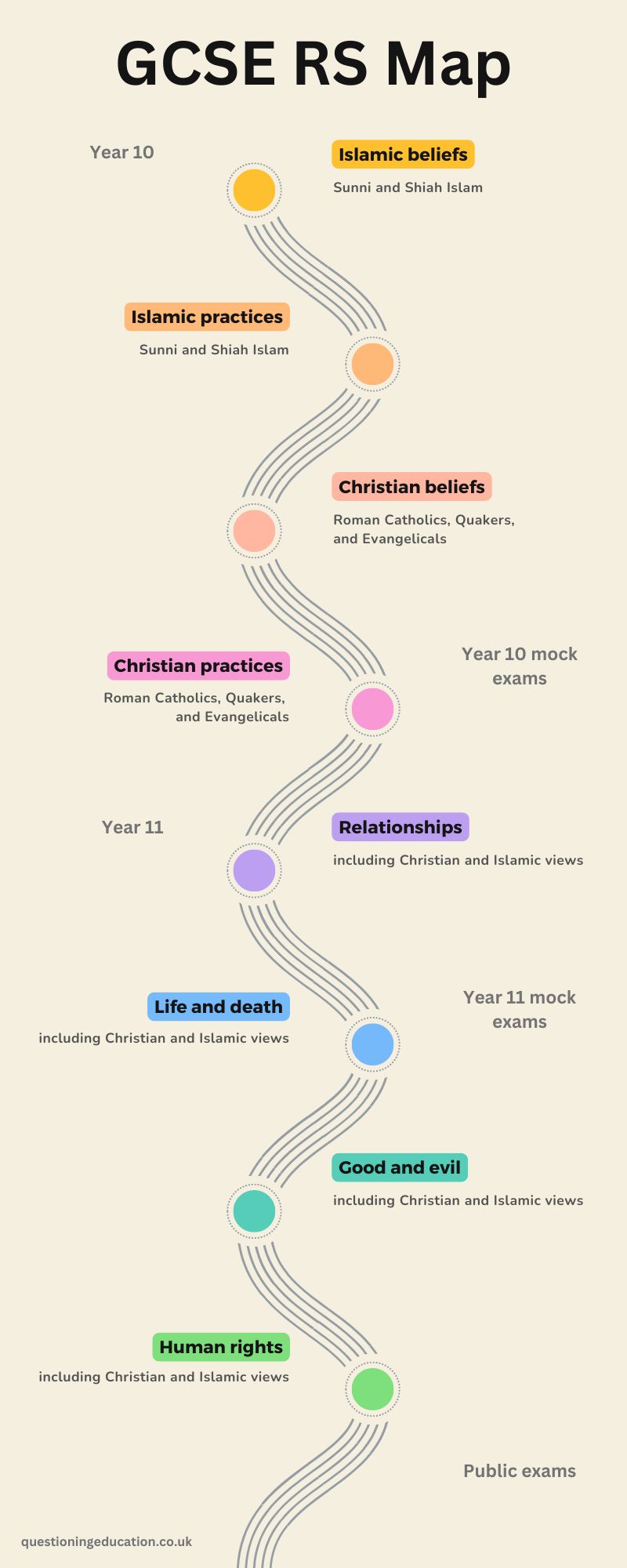
We do the Eduqas GCSE (Full Course) in RS: Route A3 (Component 3 Option 3: Islam) (C120P3).

Units
The GCSE has three parts:
- Ethics (2 hour exam)
- Christianity (1 hour exam)
- Islam (1 hour exam)
Public exam dates (2025)
- Ethics: Tuesday 13 May 2025 (morning)
- Christianity: Wednesday 21 May 2025 (afternoon)
- Islam: Wednesday 4 June 2025 (afternoon)
Source: Eduqas
- GCSE results day: Thursday 21 August 2025

Mock exam dates
You do mock exams in the sports hall with your year group.
Year 11
| Date and time | Component | Units |
| Thursday 5 December 2024, 08:20 am | Ethics (1 hour) | Life after death, Good and evil |
| Thursday 12 December 2024, 12:50 pm | Christianity (30 minutes) + Islam (1 hour) | Christian beliefs + Islamic beliefs, Islamic practices |
Year 10
Year 10 mock exams take place in the summer – we’ll post details when they are fixed.
Revision session dates (Year 11 only)
We’ll post these on the site when the dates are fixed.

Topic lists
Student-friendly lists of all of the topics for each unit.
Note: Ethics topics lists will be put here later in the term.
Key words (2 mark questions)
The words and meanings you need for all possible 2 mark questions.
| Unit | Quizzes | Words only | Meanings only | Words and meanings |
| Christianity | Quiz 1, Quiz 2, Quiz 3 | Words | Meanings | Glossary |
| Islam | Quiz 1, Quiz 2, Quiz 3 | Words | Meanings | Glossary |
All key words
This section is about all of the key words listed on the syllabus (including the ones you need for the 2 mark questions). There are a lot!
| Unit | Quizzes | Words | Words and meanings |
| Christian beliefs | Quiz | Words | Glossary |
| Christian practices | Quiz | Words | Glossary |
| Islamic beliefs | Quiz | Words | Glossary |
| Islamic practices | Quiz | Words | Glossary |

Past exams
| Year | Ethics | Christianity | Islam |
| 2023 | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme |
| 2022 | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme |
| 2021 | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme |
| 2020 | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme |
| 2019 | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme |
| 2018 | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme | Exam, mark scheme |
Past question grids are available from your RS teacher.
Sample assessment material are here but it’s not all relevant to you.
Note: the 2024 exams are not yet publicly available to students.
Literacy marks
You get marks for spelling, punctuation, and grammar (spag): up to
- 6 marks, paper 1 (Ethics), question 1d
- 6 marks, paper 2 (Christianity), question 1d
Our grade boundaries
For end of unit exams, marked out 30, we’ll use these:
| Grade | Mark |
| 9 | 27 |
| 8 | 25 |
| 7 | 23 |
| 6 | 20 |
| 5 | 18 |
| 4 | 15 |
| 3 | 11 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 1 | 4 |
Boundaries for mock exams will be set only after you’ve sat those exams.

‘Religious traditions’

In the exam, ‘religious tradition‘ usually means a group in a religion.
- In Christianity, this could be Roman Catholics, Quakers, and Evangelicals
- In Islam, this could be Sunnis and Shias

Other useful resources
We recommend that you use the excellent BBC resources:






